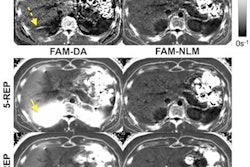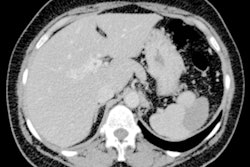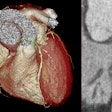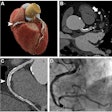
Nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis (HS) on nonenhanced CT is significantly associated with the presence of high-risk plaques on coronary CT angiography (CCTA), as well as future cardiovascular events, according to news from the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.
Concurrent evaluation of nonalcoholic HS with CT during CCTA of 1,148 patients in Japan with suspected chronic coronary syndrome led to more accurate detection of those who were at high risk of major adverse events, including cardiac death, acute coronary syndrome, and late revascularization.